- Non routine
- Non repetitive
- One off
- Goal
- Group of related projects
- Coordinated together for more benefits
- Related or not related projects and programs
- They may not be directly relaxed
- Triple constraints : time , cost , scope
- Diamond constraints : TCS + quality
- PMBOK's constraints : identifies diamond constraints + risk resources , there may be more than six constraints in a projects
- Among all constraints , only two are considered independent
Project tries to achieve an expected level of performance by spending a limited funds and time are agreed in scope of projects.
Management : cost of getting together efficiently and effectively.
Project management :
Product management : management of aspects of products
Venture management : focus on creative , innovative and challenging business ideas.
Stakeholders:
- Impacted by over project
- Exist influence over project
- Successful people must acheive goals and expectations of its stakeholders.
- Project sponser
- Project manager
- Pm team
- Business partner
- User/consumer
- BOD / shareholder
- Society
- Holds pm accountable
- Will be involved in taking decision for high risk stages
- Provides statement of work to PM . statement of work is detailed description of objectives of project.
- Authority one project
- Responsibility for achieving goal
- Attributes and duties : all positive
- Should be self directed and cross functioned.
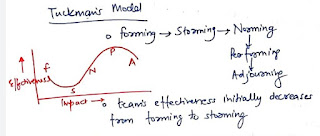
Tuckmanis model:
- Team effectiveness initially decreases from forming to storming.
Conflict resolution:
- Confronting / colabrating leads to a win win situation as a person shows both assertiveness and cooperation.
PMO
- Office for managing project
- Control of PMO increases from supportive , controlling to directive PMO style.
Organisation structure:
Functional manager:
- Expert in fuctional area.
- Supervises over department
- Responsible for skills development and employee annual appraisal
Functional organisational structure:
- Grouping by specialisation
- Team member reports to both PM and FM
- Most suitable when long line of communicating
- Organisation offers limited range of prodcts
- Person can work on many projects + upgrade his skills
Disadvantage:
- Response to customer is slow
- Difficult to fix accountability on project
- Unsuitable for geographically scattered organisation
Projectised structure
- Resources report to PM only
- PM has full authority
Advantage: centralised authority - faster completion
Disadvantage : may become arrogant , may suffer communication , employee's skill upgradation suffers
Matrix structure
- Blend of projectised and functional
- Member spends time on project as well as fuctional area
- It balances performane on project as well as skill upgradation
Project process group and knowledge area
Life cycle:
- Sequence of project phases
- Not cyclical in nature
- No two projects are exactly same as they vary in details , but all projects follow similar life cycles.
- PMBOK identifies 49 processes for project completion which are grouped into 5 process group and 10 knowledge areas.
Process groups:
- Process is series of activities
- I-P-E-C-C
- Project groups are not group phases generally
- Every project of phase will have all the process groups in it
Knowledge area
- Skill set
- Project character , project management plan - integration
- Creating work breakdown structure - scope
Note:
- Project feasibility , appraised and selection must be completed before starting negotiation
- Project character is developed by project sponsor based on business case development.
- Project management plan , also called integrated base line contains management plans of all knowledge areas. It is comprehensive plan based on which entire project is executed.
- Detailed project report is a planning phase outcome document.
- Desirable - it is tangible / intangible good or service to be handled over which form part of project outcome.
Analysis of project phases:
Product life cycle : after project we move to operation phase where product sees market.
Prototyping : several working models of intended products are developed and tested under real life condition.
Phase to phase relation:
- Sequential
- Overlapping / parallel
- Iterative
Concurrent engineering:
- Simultaneously engineering
- Stages run in parallel
- Decreases product development time
Types of software development:
- Predictive life cycle / waterfall model
- Iterative / increamental life cycle
- Agile / adaptive life cycle
Waterfall model:
- TCS determined in detail early stage
- Has comprehensive plan which is not expected to change
Incremental/ iterative:
- Scope not defined in detail at initial stages
- Used where changes are expected
Agile/adaptive:
- Used when changes are rapid
- There is review of work after every iteration
Project initiation
- Also called as conception / selection phase
- Initial scope is defined , stakeholders are identified and project charter is prepared
- Outlines aim of project
- Should be smart
- Project charter translates project sponser business case into project objective.
- Business case contains justification for the project
Opportunity study:
- Indicative
- Used to generate new ideas
- Can use techniques like SWOT analysis , brainstorming
Pre feasibility study:
- It is screening of ideas
- Recommended when formulation is costly
- Should not take more than 3 months
- Able to decide regarding investment
- Analyse as many factors as possible
Feasibility study:
- More rigorous
- Specialised skills
- Requires highly reliable data
Project appraisal
- Evaluation of overall project
Project selection
- Can be selected using numeric or well as non numeric model
Note: comparitive benefit model is non numeric selection.
Technical feasibility
- Consideration of technology and its effect on production system
- Factors like location , plant size , plant layout , construction , equipments , infrastructure, etc.
- Location cost index (LCI) should be < 100
Factors considered for selecting technology:
- Affordability
- Compatibility
- Accessible
- Operation safety
- Gestation period















0 Comments