Fluidity
Spiral test
- Sprue in vertical plane ,spiral in horizontal plane.
- Ability of the liquid metal to flow into the cavity is known as fluidity.
- It is the property of liquid metal.
- Distance travelled by liquid metal before solidification in a standard spiral will be the index of fluidity.
- It is the minimum cross sectional area in all the gating elements ,it will control the flow of the liquid metal in the cavity. It is a first parameter to be calculated in all the gating elements.
- Choke area is at the bottom of the sprue. Velocity of the liquid metal which is enter into the cavity is less. There is no turbulence and splashing. It can be used for casting of non ferrous material. There is a possibility of air aspiration. Casting yield will be less.
- Choke area is at the gate. Velocity of liquid metal which is entering into the cavity is very high. There is turbulence and splashing of the liquid metal. It can be used for casting of ferrous material. There is no possibility of air aspiration , casting yield is more.
Solidification time
- For a given volume of the riser, sphere has having minimum surface area to volume ratio.
- But it is not used as a shape of the riser. This is due to availability of liquid metal in the spherical riser at the centre.
- To put the pressure on casting which increase the density of casting .
Riser design
Methods to increase the performance of riser
- If intersection of lines take place above or on the curve the casting is free from defects called sound casting. If not then casting has some defects called defective casting.
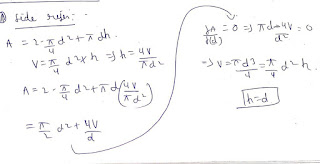
Question : calculate dimension of cylindrical blind side riser h=d to produce a casting of dimensions 60 x 14 x 20 centimetre cube . Riser solidification time is 25% greater than solidification time of the casting. Use chovrinov's rule of solidification.
- For uniform thickness and simple shape of the casting 1 riser is sufficient to compensate the shrinkage and it is positioned on the top of the cavity at the centre.
- For non uniform thickness of the casting riser is provided close to the higher thickness of the casting.
- For minimum thickness and maximum surface area of the casting to compensate the fast rate of shrinkage of material more number of risers are required.
- At minimum cross section in the mould cavity to maximize the heat transfer rate and to provide uniform and directional solidification metallic objects are provided known as chills.
- To minimise the erosion and to maximize the heat transfer rate at a critical cross section in the mould cavity , metallic objects are provided. These are known as padding .
- By providing chills and padding directions solidification can be possible.
- Expendables moulds
- Sand moulding
- Shell moulding
- Investment casting
- Full moulding
- CO2 moulding
- Permanent moulds
- Centrifugal die casting
- Slush casting
- Squeeze casting
- Continuous casting
- Molding material are fine-grained dry silica, Phenolic resin ,alcohol.
- Applications : cylinder block of IC engine , Rocker arms , valve plates of refrigerator.
- Pattern is provided by metallic material and it will be heated up to 250 degree Celsius.
- Moulding material made in contact with metallic pattern, due to heat from the pattern by activating the bonding properties of phenolic resin moulding sand will be stick to the surface of pattern in the form of shell.
- Thickness of shell will depend on contact time between pattern and moulding material known as dwell time.
- After getting required thickness of shell , pattern and shell will be heated up to 300 to 350 degrees celsius and by using injection pins shell will be separated from the pattern by adding number of shells together required cavity be produced into which liquid metal is allowed to solidify.
- Accuracy and surface finish of casting is more .
- It can be used for mass production.
- Amount of molding material is less.
- It is an expensive process generally used for small size castings.
- Application : in gas turbine blades, jet engine parts and medical implants , dentures ,gold ornaments , etc.
- Pattern is produced by wax material.
- By adding number of wax patterns along with gating elements pattern assembly can be produced.
- By dipping the pattern into the slurry material ,fine grain ceramic metal can be added to produce a ceramic shell, this process will be repeated until required thickness of ceramic shell can be produced known as stuccoing process.
- By heating the ceramic shell ,wax will convert into liquid form and it will be removed from the shell to get the required cavity into which liquid metal will be allowed to solidify .
- To minimise the gas defect this process is carried under vacuum.
- Complex shape of the objects with high melting point material with more accuracy can be produced.
- It is an expensive and time-consuming process used for small size casting only .
- Pattern material: plastic ,polyesterene , foam , PVC , thermocol ,etc.
- Applications : tooling, fittings, motor casing.
- Pattern is produced by plastic material.
- Gating elements will be added to the pattern.
- By adding resin binder on the pattern , silica sand will be added and it will be supported by providing baking sand.
- Liquid metal is directly allowed on the pattern ,due to high temperature pattern will start evaporation and it will convert into gaseous form by allowing the gases to escape, cavity can be produced into which liquid metal is allowed to solidify.
- If the mould is prepared by pop then it is called plaster molding ,generally used for low melting point non ferrous materials.
- Cost is low.
- To prepare large mould and cores this technique can be used. Mould is prepared by adding sodium silicate binders ,CO2 gas will be supplied to the mould ,it will react with sodium silicate and produce silica gel which is having better bonding properties, due to this strength and hardness of the mould can be increased.
- Strength of the mould will depend on time of supplying CO2 gas, to the mould known as CO2 gassing time.
- Applications: machine tool bads ,turbine housing ,large size gear blanks, large size mould.
- Application : hollow cylinder pipe ,gun barrels, large size bushes, tubes, propeller shaft, cylinder liners, etc .
- To produce hollow object without using the core this technique can be used. Liquid metal is allowed through a rotating die ,due to centrifugal force and fast rate of cooling, fine grain structure with the high density can be produced.
- It can be used for mass production. Accuracy and surface finish is high.
- It is generally used for hollow axis , symmetrical and cylindrical shape of the object only.
- Casting yield is 100%.
- Continue the rotation until the metal solidfies.
- Applications: pulleys , wheels ,small size flywheel, spoked wheel ,etc.
- Liquid metal is enter into the centre of rotating die by means of gravity force and it is forced away from the centre by means of centrifugal force, high density pure metal will be forced away from the centre and less density impurity collected towards the centre.
- Production rate is high.
- Casting yield will be hundred percent for centrifugal and less than hundred percent for semi centrifugal.
- Number of cavities are produced on a die along with the grating element. Liquid metal is enter into centre of die by means of gravity force and it is forced away from the centre by means of non-uniform centrifugal force known as centrifuging.
- Unsymmetric objects in mass production can be produced.
- Axis of rotation of the mould not coincide with the axis of the object.
- Casting yield is less .
- Application: pattern used in investment casting , other unsymmetric shapes of the object.
Gravity die casting
- Liquid metal is entered into the die cavity by means of gravity force.
- It is used to produce simple shape of the object only.
- Accuracy and surface finish is very high due to fast rate of cooling, Fine grain structure is produced which are having more strength and hardness.
- Production rate is high.
- Applications : pistons used in automobiles made of aluminium and its alloys and other simple shape of the object.
- Tool steel, die steel for die material
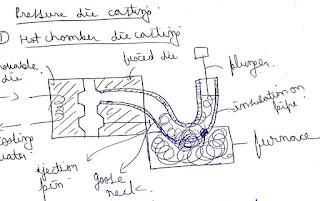
- Liquid metal is enter into the cavity under external pressure ,furnace is integrated with die.
- It is used to produce complex shape of the objects which are made up of low melting point material like lead ,tin and zinc ,due to sticking tendency of aluminium life of goose neck will be reduced that's why aluminium is not used.
- Aluminium is not used in this technique.
- Production rate is very high.
- Accuracy and surface finish of casting are more.
- Metal is getting solidified under external pressure.
- High dense structure with better mechanical properties can be produced.
- Furnace is separated from the die.
- It is used to produce complex shape of the object which are made up of aluminium or copper, brass etc.
- It is not used for ferrous materials.
- Production rate is high.
- Applications : carburettors ,valve bodies, crank cases , fuel injection pump part , toilet fixtures, etc.
- Thin castings , hollow thin castings, statues, decorative items , thin ornaments ,etc.
- To produce thin castings and hollow thin casting of required thickness ,this technique can be used ,liquid metal is allowed to solidify on the die. After getting required thickness by rotating the die and solidified metal can be separated from solidified metal.
- This is known as partial solidification.
- Generally used for low melting point material like lead, zinc ,aluminium ,copper etc.
- Liquid metal is allow to solidify on the die by applying external plunger pressure ,metal is getting solidify between plunger and die.
- Shape and size of the casting will depend on shape and size of plunger and die and it will also depend on external pressure applied by the plunger. It is a combination of casting and forging.
- Better mechanical properties can be produced.
- Application : brake shoes made up of aluminium , bushes made up of brass and bronze.
- Long length bars , rods ,billets etc.
- Liquid metal is allowed through the die opening , output of the die is a solid crust on which water will be sprayed to cool the material at a faster rate.
- Die is made up of copper material ,production rate is high.
- For melting of low melting point non ferrous materials in small scale industries, this can be used.
- By melting pig iron large quantities of cast iron can be produced in mass production. It is easy to operate. Cost of melting is less.
- If preheating mechanism is used to increase the temperature of the air which is supplied to the furnace from 200 to 400 degrees celsius is known as hotblast cupola.
- It is ratio between metal to fuel.
- This ratio is generally in the range of 4:1 to 12:1.
- Coupola furnace this ratio is 10:1.
- By melting pig iron, large quantities of steel can be produced. Melting rate is very high.
- Heat transfer losses will be less. Cost of melting is more.
- Heat required for melting can be produced based on induction principle. By melting the pig iron steel can be produced. It can be used for non ferrous materials also. Melting rate is very high. It is very compact. Cost of melting is more.
- Blow holes and open blows : gas defects which are formed on the surface of the casting are open blow and which are formed inside the casting are blowholes.
- Scar : a shallow blow which is formed on the surface of the casting.
- Blister: it is a scar cover by thin layer of metal.
- Pinhole porosity : small size gas holes which are formed due to hydrogen gas.
- Drop and dirt : due to improper ramming loose silica sand particles will drop from box to drag box will form a projection on the casting known as drop and the cavity on other side of casting known as dirt.
- Cuts and washes : at minimum cross section in the mould cavities due to lack of ramming and improper gating design ,projection can be formed known as cuts and washes.
- Scab : due to improper ramming liquid metal can be penetrate into loose sand layers in the box will form a projection known as a scab.
- Rat tail :due to improper ramming and mixing of sand due to lack of hardness by the expansion of mould at a given cross-section, small projection can be formed known as rat tail.
- Swell : due to improper ramming along the surface of the mould ,by the expansion of the cavity projections can be formed on the casting known as swell.
- Shrinkage cavities: due to improper riser design cavity is formed due to shrinkage of the material is known as shrinkage cavities.
- Misrun : due to lack of fluidity before reaching the extreme end of the cavity, liquid metal is getting solidified will form a defect known as misrun.
- Cold shut: two streams of liquid metal will not fuse properly will form a discontinuity in the casting.
- Hot tears or cracks : due to non uniform cooling ,internal stresses can be developed in the casting. If the stresses will be more than the strength of the material cracks will be formed.
- Mould shift : due to improper positioning of cope box on drag box there is a shift along the parting line.
- core shift: shifting of the core from its original position due to buoyancy force.
Shot blasting: to remove silicon carbide (hard and brittle ) particles which are fused on the surface of casting , hardened steel balls will be forced on the casting.
Sand blasting : if coarse grain silica sand will be used for cleaning for castings (hollow thin castings).











































0 Comments