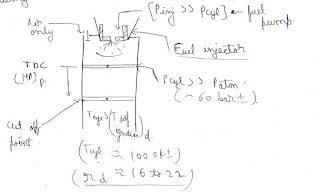
Working of 4 stroke engine
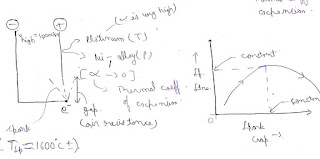
Spark plug
- For sparking high voltage is required to overcome the air resistance present in the spark gap.
- Theoretically platinum is the best suitable material but practically spark plug should be made up of nickel alloy because its thermal coefficient of expansion tends to zero.
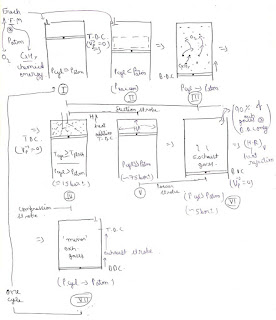
- After power stroke as the exhaust valve gets opened the major exhaust gases will escape out of the cylinder at BDC only (heat rejection at constant volume) ( figure 4 ).
- After heat rejection the remaining exhaust gas will be thrown out of the cylinder as the piston moves from BDC till TDC (exhaust stroke).
Engine material selection
- Piston rings : it should be made up of silicon cast iron or silicon steel so that it will be smooth as brittle. Brittle because if it is ductile then after some usage time it will deform and create a space from where AFM leaks out.
- It is subjected to fatigue loading conditions and it should be made up of ductile material by forging.
Air standard assumption
- Air is only working fluid.
- Perfect gas
- Ideal gas equation.
- CP ,CV and specific heat should be constant.
- Heat addition: the internal combustion is modelled as heat addition into the system from an external source.
- Heat rejection : the exhaust process in which majority of exhaust gas escape out of the cylinder is modelled as heat rejection.
- Process ratio

- Efficiency of otto cycle
- Maximum work done condition (Otto cycle) : T1 and T3 is considered to be the constant because T1 is assumed to be depend upon the atmospheric condition which is not going to be affected by any process parameter and T3 is restricted due to the temperature resistance of any material .
- It is an imaginary pressure which will provide the same work done as the actual cycle for the same change in volume .
- It is the branch of science in which there is a study of transformation in chemical energy of the fuel into its thermal form due to the oxidation reaction of combustion.
- Note: the total amount of time required for the chemical reaction or time from the beginning of spark into beginning of ignition is termed as chemical delay.
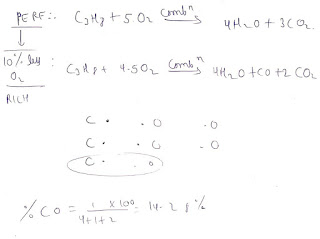
Perfect combustion
- When the combustion of the fuel mass in such a manner that there is no fuel remaining in any form no there is any oxygen left.
LEAN
PERFECT
RICH
SUPER RICHNote : exhaust gas analysis (lean AFM)
ORSAT analyser
- It is a device which is used to absorb the exhaust gases from an IC engine and gives the volumetric percentage analysis of dry air exhaust.
- It is defined as the ratio of fuel air ratio in actual combustion condition with respect to the theoretical combustion condition.
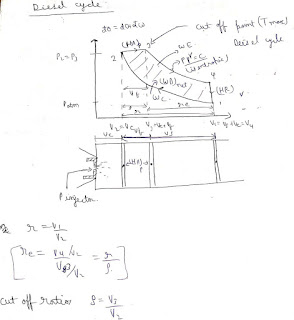
- In diesel engine only air is entered into the cylinder during the suction stroke and due to the very high compression ratio the temperature inside the cylinder after compression becomes more than the self ignition temperature.
- Hence as the fuel enters the cylinder it starts its ignition and during that time period piston displaces and it is assumed as heat addition at constant pressure.
- Fuel is injected into the cylinder by the use of heavy pressure difference and as the opening is rough the fuel mass is a split into the smallest possible size called atomization.
- After atomization the surface area increases and due to which fuel state changes from liquid form to its vapour called vaporization.
- After vaporization the fuel mass is enforced uniformly mix up with the air molecule to create a air fuel mixture called uniform distribution.
- The total time required from the beginning of the injection of the fuel to the beginning ignition of the fuel is termed as ignition delay in CI engine.
- Whereas the total time from the beginning of the sparking to the beginning of ignition is termed as ignition delay or chemical delay in SI engine.
- The total time required for the atomization ,vaporization and uniform distribution of air and fuel mixture is termed as physical delay.
Explosion ratio
Note :
- Heat added at constant volume should be less then heat at constant pressure because already the pressure inside a cylinder is high. If heat addition at constant volume increases then it will increase the T3 and that may cause the cylinder explosion.
Part 1
Heat added
- The total amount of thermal energy or power available from the fuel due to the combustion of 1 kg of mass is termed as calorific value.
- Due to the expansion of the air pressure and volume changes which is found from the PV diagram indicated diagram is termed as indicated power.
- It is the input energy or power available at the piston of reciprocating motion.
- The total amount of power on energy available at the end of engine shaft of rotary motion which is found by using brake mechanism.
Thermal efficiency
Engine performance parameters Relative efficiencyNote:Question :the pressure at 25% of the stroke is 1.4 bar whereas the pressure at 75% of the stroke is 4.2 bar ,on the compression curve following PV^Gama = constant. Assuming the ratio of specific heat is equal to 1.4 then determine compression ratio,Air standard efficiency of the Otto cycle, If the relative efficiency is 50% and engine develops the brake power of 25 KW then determine the rate of fuel consumption in KG per hour if calorific value is 42 megajoule per kg .
Question :following data refers for the four stroke for cylinder petrol engine having bore of 11 cm and stroke length of 30cm. The engine speed is 2250 RPM. The total brake power load on the engine is 30 kg at the drum radius of 0.6 m. The total frictional losses in an engine is 12.5 KW and the rate of fuel consumption in the engine is 10.5 kg per hour. The calorific value of the fuel is 45 mega joule per kg. The ratio of the specific heat is 1.4 and the ratio of clearance volume and swept volume is equal to 0.1. determine brake power,Mechanical efficiency,Brake thermal efficiency,Brake mean effective pressure ,air standard efficiency, Relative efficiency.
Actual suction process
- After heat rejection the piston displaces from bdc to tdc to thrown out the remaining exhaust gases out of the cylinder.
- At very near to the end of exhaust stroke , exhaust stroke valve will get close down , hence for the remaining gases exhaust stroke it compresses the exhaust gas.
- At the beginning of suction stroke there will be no entry of the fresh air fuel mixture as the pressure inside the chamber is slightly above the Patm.
- Hence some pistion displacement is wasted during the suction stroke until the pressure inside the cylinder reaches to Patm , then the actual suction begins .
- It is the ratio of the actual volume of air that entered into the cylinder during suction stroke to the theoritical swept volume.















































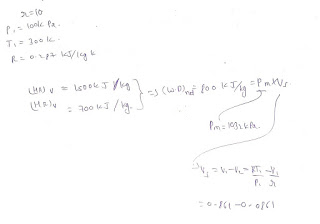









0 Comments